Cubic Yard Calculator
Professional-grade cubic yard calculator for construction, landscaping, and earthwork professionals. Calculate volume, weight, and cost with industry-standard accuracy.
How Cubic Yard Calculations Work
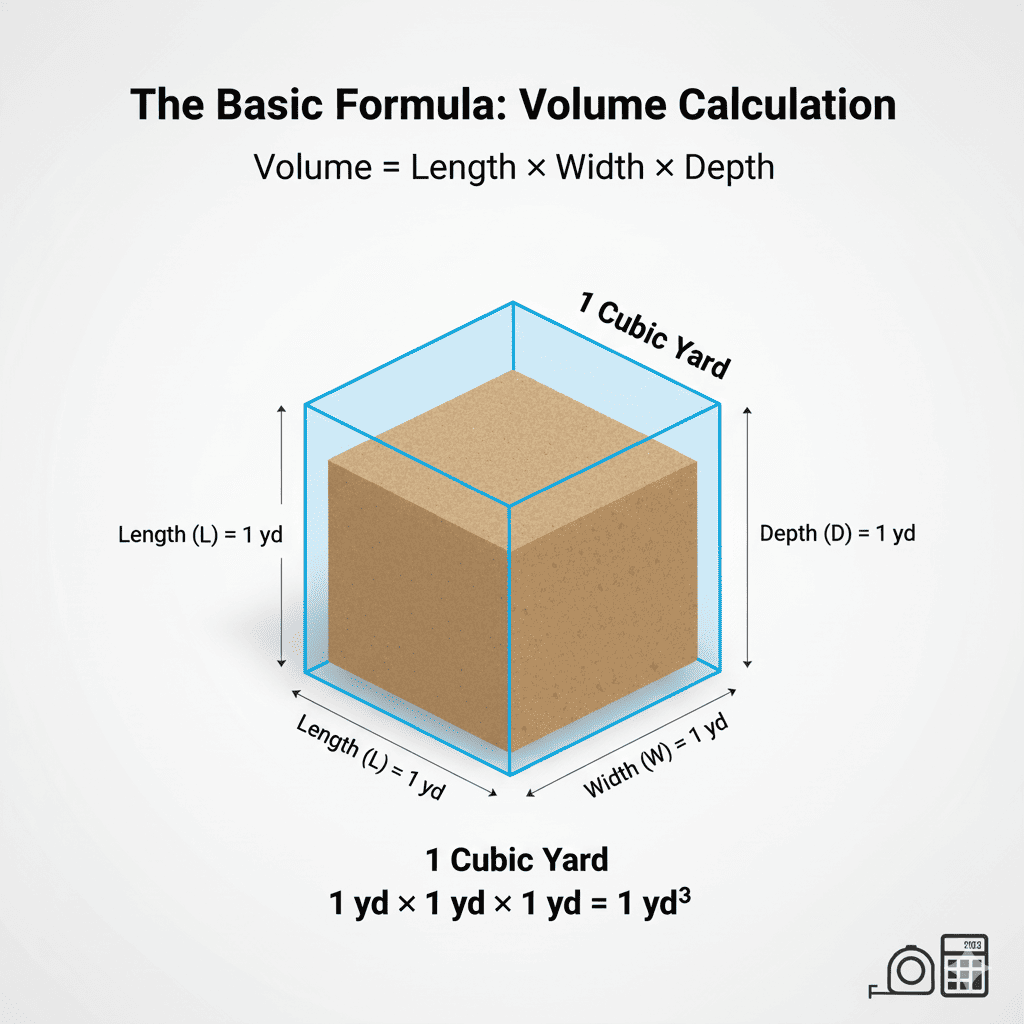
The Basic Formula
Cubic yard volume is calculated using the simple formula: Length × Width × Depth. However, professional calculations require unit conversions and material considerations.
Understanding Scale
What Does 1 Cubic Yard Look Like?
One cubic yard equals 27 cubic feet. That's roughly the size of a standard washing machine or a small refrigerator. Understanding this scale helps you visualize your project needs.

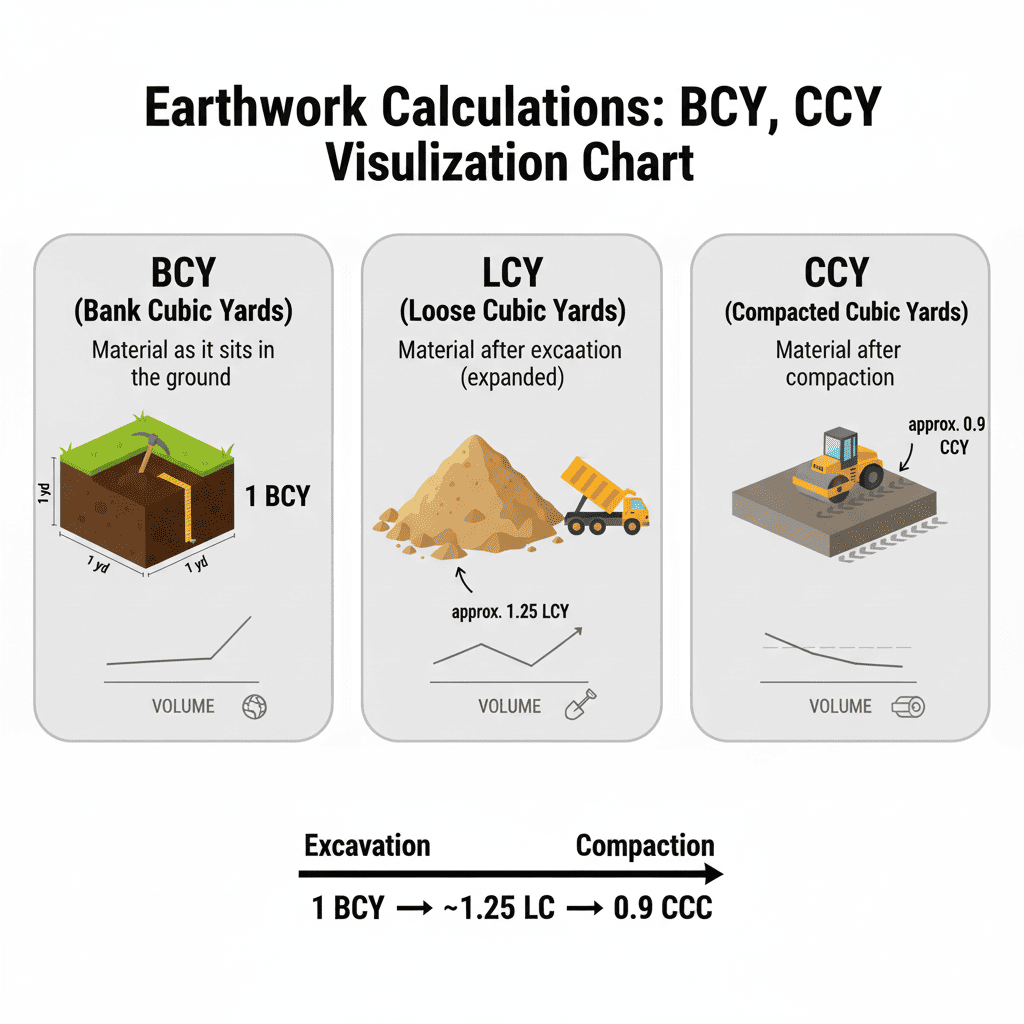
Earthwork Calculations: BCY, LCY, CCY
Material as it sits in the ground
Material after excavation (expanded)
Material after compaction
Technical Insights: Understanding Bulking and Compaction
Bank Cubic Yards (BCY)
Material volume in its natural, undisturbed state in the ground. This is your starting point for excavation estimates.
Loose Cubic Yards (LCY)
Volume after excavation - material expands due to air pockets. Typically 20-30% more volume than BCY for most soils.
Compacted Cubic Yards (CCY)
Volume after compaction - material is densely packed. Usually 15-25% less volume than BCY for fill materials.
Key Formula: BCY × Bulking Factor = LCY | CCY × Compaction Factor = BCY Always verify factors with your specific soil conditions and equipment.
Complex Shapes & Irregular Areas
Real-world projects rarely have perfect rectangular shapes. Learn how to break down irregular areas into manageable geometric shapes for accurate calculations.
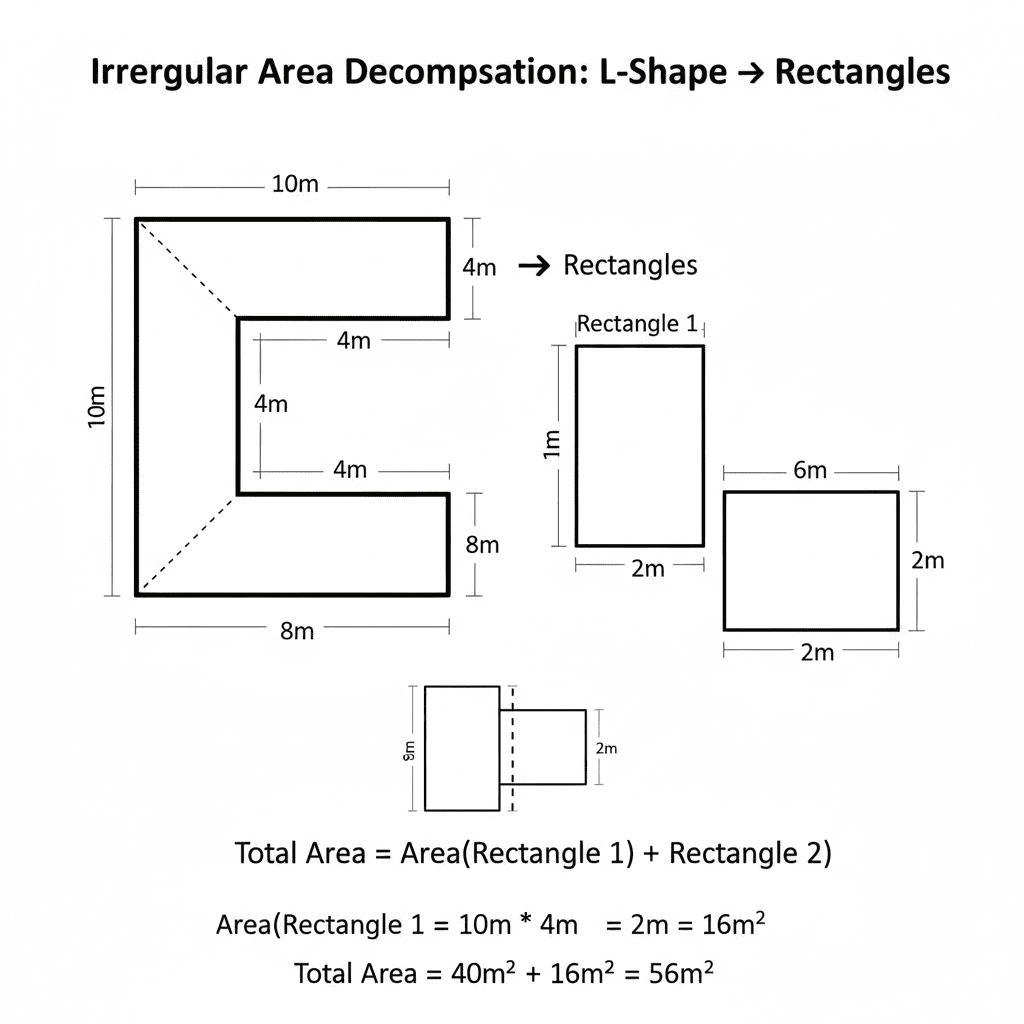
How to Decompose Irregular Areas:
- Identify the shape: Break down complex areas into basic geometric forms (rectangles, triangles, circles)
- Calculate each section: Measure and calculate volume for each geometric component separately
- Sum the volumes: Add all individual volumes together for the total project volume
- Example: An L-shaped patio becomes Rectangle A (10×8×0.5 ft) + Rectangle B (6×4×0.5 ft) = Total volume
From Volume to Order: CY-to-Tons Conversion and Pricing
Understanding Density Factors
Different materials have different densities, which affects how much they weigh per cubic yard. This is crucial for ordering the right amount of material by weight.
Common Material Densities:
- Gravel: 1.4 - 1.6 tons per cubic yard
- Sand: 1.2 - 1.4 tons per cubic yard
- Topsoil: 0.8 - 1.0 tons per cubic yard
- Concrete: 2.0 - 2.4 tons per cubic yard
Weight-Based Ordering Process
Pro Tip: Always order 5-10% extra material to account for waste, compaction, and grading. Most suppliers sell by the ton, so accurate weight calculations prevent costly shortages or excess.
Advanced Material Density and Conversion Factors
Professional material estimation requires accurate density factors to convert volume (cubic yards) to weight (tons). The table below provides industry-standard conversion factors for common construction and landscaping materials.
| Material Category | Example Material | Typical Loose Density (lbs/cy) | Volume-to-Weight Factor (Tons/CY) | Notes on Density Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine Aggregate/Concrete | Sand (Loose) | 2,700 – 3,200 | 1.35 – 1.6 | Density fluctuates significantly based on moisture content (bulking). Professional concrete factor is often 1.5. |
| Coarse Aggregate | Gravel/Crushed Rock | 2,500 – 2,900 | 1.3 – 1.5 | Factors for specific base materials (e.g., 304, 411) can increase up to 1.75. |
| Soil/Fill Dirt | Topsoil (Loose/Dry) | 2,000 – 2,700 | 1.0 – 1.35 | Dependent on composition, moisture, and organic content. |
| Organic Material | Mulch/Woodchips | 400 – 800 | 0.2 – 0.4 | Lightest category; primary metric for sales is volume, not weight. |
Note: These factors represent typical ranges. Always verify with your specific supplier for exact density values, as local material variations can affect these numbers. Use the custom density input in our calculator for precise calculations.
Earthwork Conversion Factors (Bulking and Compaction)
Earthwork calculations require understanding how soil behavior changes during excavation and compaction. Use these industry-standard factors for accurate project planning and material logistics.
| Material | Typical Bulking Factor (LCY/BCY) | Typical Compaction Factor (CCY/BCY) | Bank Density (lb/yd³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | 1.3 | 0.8 | 3,100 – 3,500 |
| Soil | 1.25 | 0.9 | N/A |
| Sand & Gravel | 1.12 | 0.88 | 3,250 – 3,500 |
| Rock (Blasted) | 1.5 | 1.3 | N/A |
Bulking Factor Application
Formula: BCY × Bulking Factor = LCY
Example: 100 BCY of clay × 1.3 = 130 LCY (30% volume increase when excavated)
Compaction Factor Application
Formula: CCY ÷ Compaction Factor = BCY
Example: 100 CCY of clay ÷ 0.8 = 125 BCY (25% more material needed for final compaction)
Professional Tip: These factors are essential for accurate trucking, disposal planning, and material procurement. Always test soil conditions on-site and consult with geotechnical engineers for large projects.
Specialized Calculators
Gravel Calculator
Calculate gravel needs for driveways, paths, and drainage
Concrete Calculator
Estimate concrete volume for slabs, foundations, and structures
Topsoil & Mulch Calculator
Calculate soil and mulch needs for gardens and landscaping
Earthwork Calculator
Professional excavation and fill calculations
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Cubic Feet in a Yard?
One cubic yard equals exactly 27 cubic feet. This is because: 3 feet × 3 feet × 3 feet = 27 cubic feet. Knowing this conversion is essential for accurate material ordering.
How Do I Convert Square Feet to Cubic Yards?
To convert square feet to cubic yards, multiply your square footage by the depth in feet, then divide by 27. Formula: (Square Feet × Depth in Feet) ÷ 27 = Cubic Yards.
What's the Difference Between Loose and Compacted Material?
Loose material (after excavation) expands and takes up more volume. Compacted material is densely packed and takes up less space. Always account for these changes when estimating quantities.
How Much Material Should I Order Extra?
Order 5-10% extra material to account for waste, spillage, and grading. For large projects or irregular terrain, consider ordering 10-15% extra to avoid running short during construction.
How Do I Calculate Depth Conversions?
Convert inches to feet by dividing by 12. For example: 6 inches = 0.5 feet. Always use consistent units in your calculations to avoid errors.
Why Do Material Weights Vary?
Different materials have different densities. Gravel is heavier than topsoil, concrete heavier than sand. Always use material-specific density factors for accurate weight and cost calculations.